X.509 Certificate (RFC5280) เป็น Digital Certificate รูปแบบหนึ่ง ใช้สำหรับรับรองความถูกต้องของข้อมูล และ กุญแจสาธารณะ (Public Key) ของเจ้าของ Certificate ตามมาตรฐาน X.509 ปัจจุบันเป็น version 3
ถ้าใครยังไม่รู้ว่า Public Key คืออะไร สามารถอ่านได้จากบทความนี้
จากกระบวนการ PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) ที่มีการใช้ Public Key ของผู้รับ ในการเข้ารหัส Symmetric Key ก่อนส่ง Symmetric Key กลับไปหาผู้รับนั้น
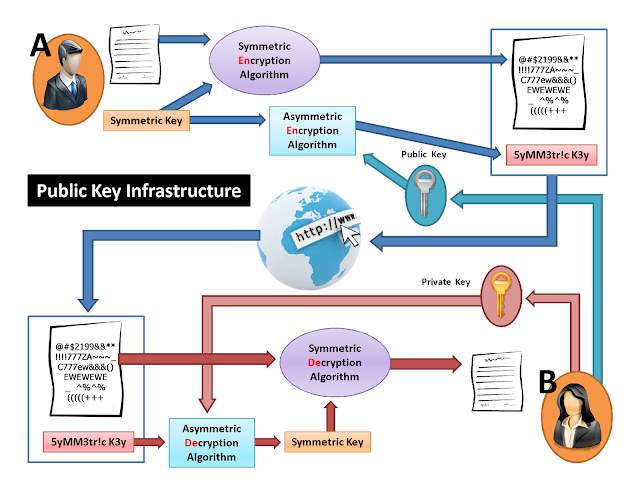
เราจะเชื่อได้ยังไงว่า Public Key ที่เอามาใช้เข้ารหัส เป็นของผู้รับคนที่เราต้องการส่งข้อมูลกลับไปหาจริง ๆ
เราไม่มีทางรู้เลยว่า ระหว่างที่มีการส่ง Public Key (ของนางสาว B) มาให้ (นาย A) นั้น จะมีการสับเปลี่ยน Public Key (ของนางสาว B) กลางทางรึเปล่า
นาย A ได้แต่เชื่อและคาดหวังว่า Public Key ที่ระบบส่งมาให้ หรือมาจากนางสาว B จะเป็นของนางสาว B จริง ๆ
จากปัญหาดังกล่าว เราสามารถแก้ได้ด้วยการใช้ X.509 Certificate มารับรองความถูกต้องของข้อมูล + Public Key ของนางสาว B
ถ้าใครยังไม่แม่นเรื่อง Public Key Infrastructure สามารถทำความเข้าใจจากบทความนี้ได้ครับ
โครงสร้างพื้นฐานของ X.509 Certificate มีหน้าตาประมาณนี้

ข้อมูลเบื้องต้น ประกอบไปด้วย
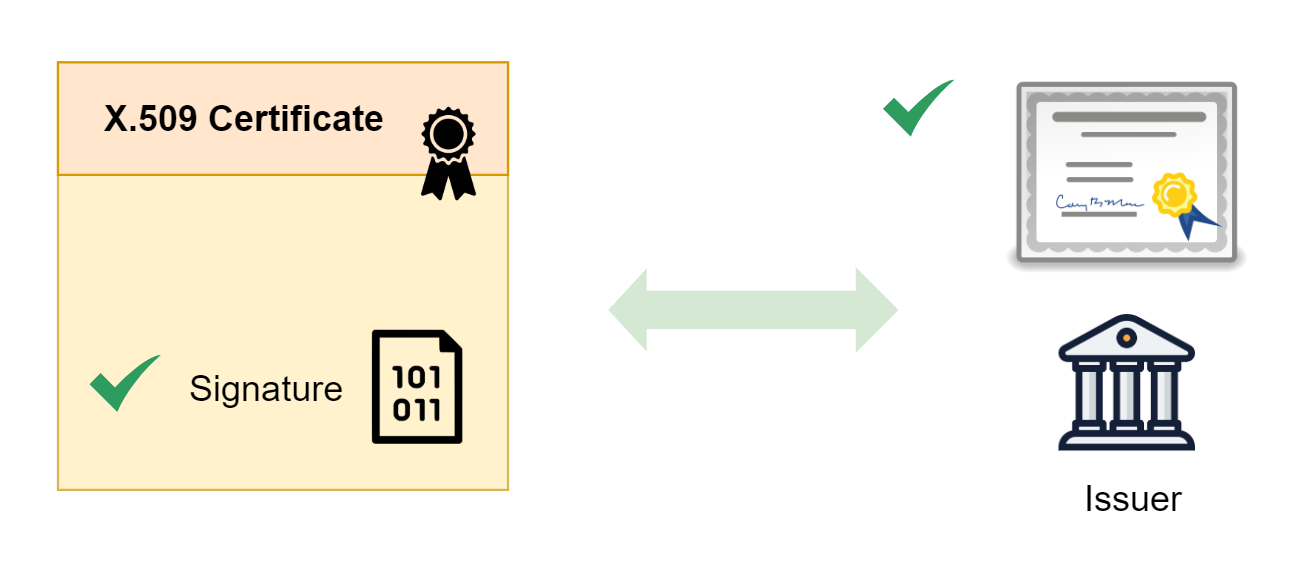
X.509 Certificate ใช้วิธีการรับรองความถูกต้องของข้อมูล และ Public Key ของเจ้าของ Certificate โดยการตรวจสอบค่า ลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอล (Digital Signature) ที่แปะอยู่ใน Certificate ว่ามีความถูกต้องหรือไม่
พร้อมทั้งมีการเช็คข้อมูลของผู้ออก Certificate (Issuer) ด้วยว่า ผู้ออก Certificate ใบนี้มีความน่าเชื่อถือ และได้รับการรับรองถูกต้องจริง ๆ
ถ้าใครยังไม่เข้าใจกระบวนการทำงานของ Digital Signature สามารถอ่านได้จากบทความนี้ครับ
อย่างที่อธิบายไว้ข้างต้นว่า การเช็คความถูกต้องของ X.509 Certificate เกิดจากการเช็คข้อมูลลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอล (Digital Signature) บน Certificate บวกกับข้อมูลผู้ออก Certificate (Issuer)
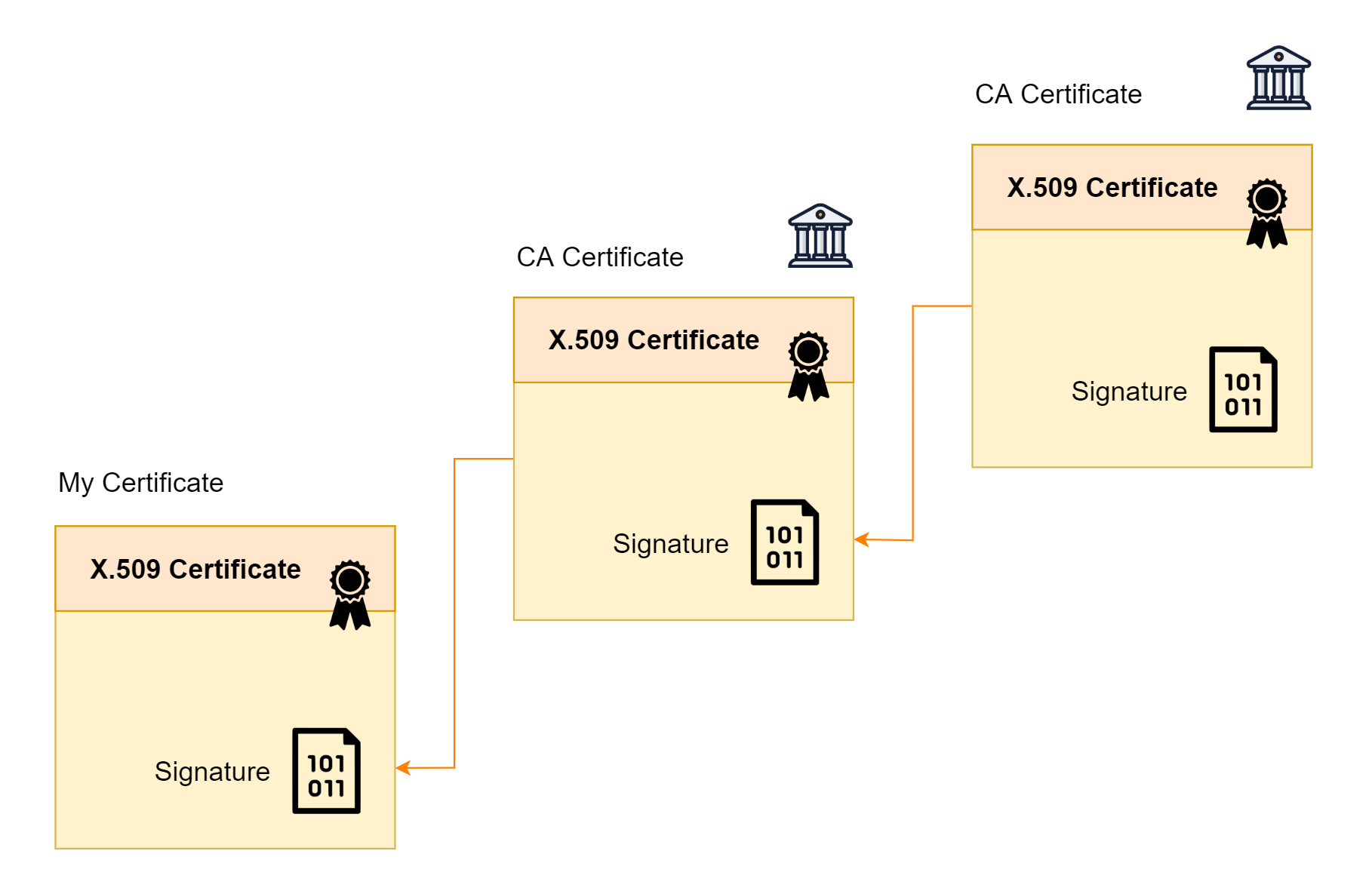
ผู้ออก Certificate (Issuer) หรือเรียกอีกอย่างหนึ่งว่า CA (Certification Authority) ก็มี X.509 Certificate ของตัวเอง
การเช็คความถูกต้องของ CA (Issuer) ก็คือการเช็คความถูกต้องของ X.509 Certificate ที่ CA ถืออยู่ เหมือนกับการเช็ค X.509 Certificate ของเรา
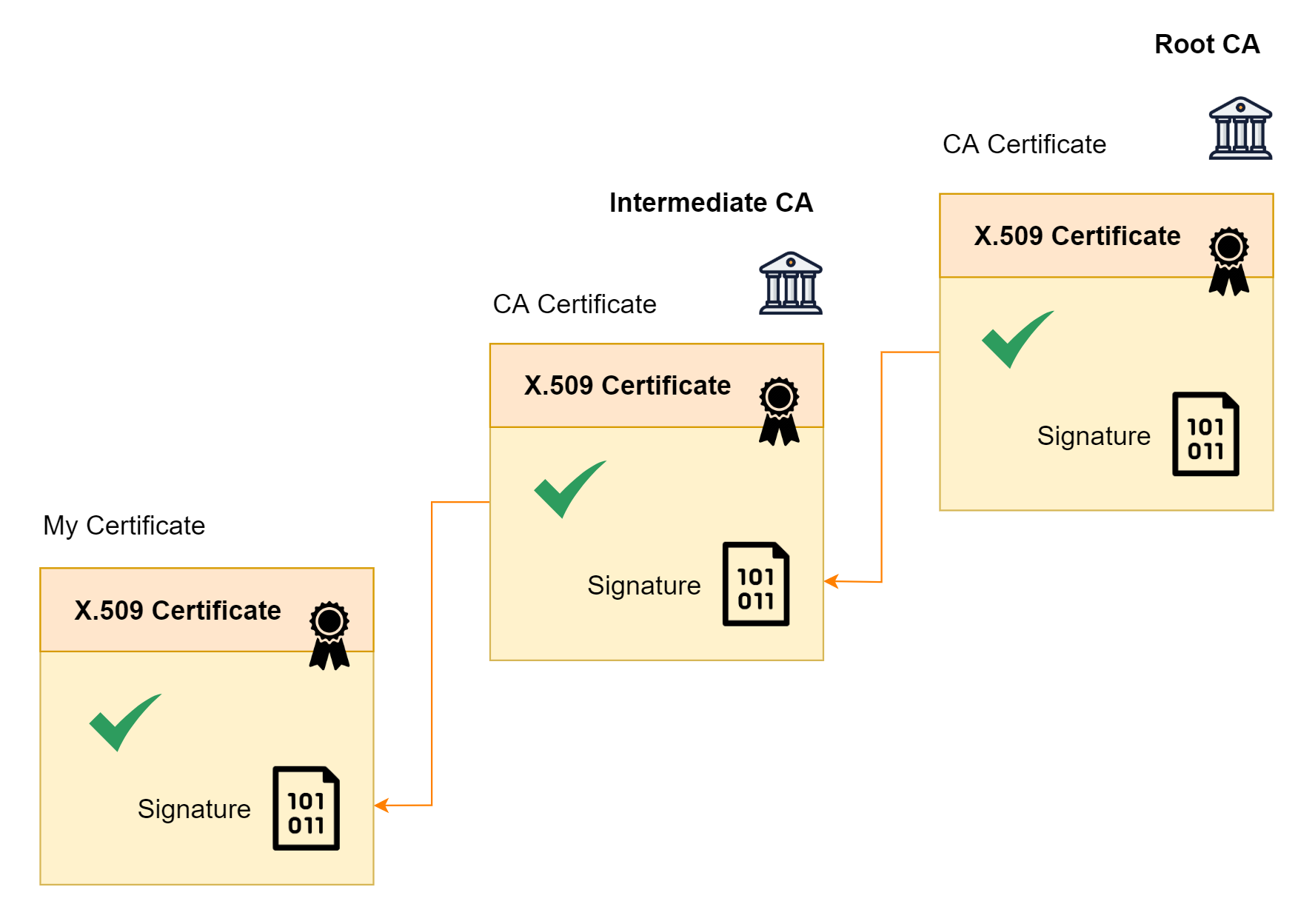
และ X.509 Certificate ของ CA เองก็มี CA อีกชั้นนึงลงลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอลให้อีก เป็นลำดับชั้นแบบนี้ไปเรื่อย ๆ ในลักษณะของลูกโซ่ หรือ Chaining
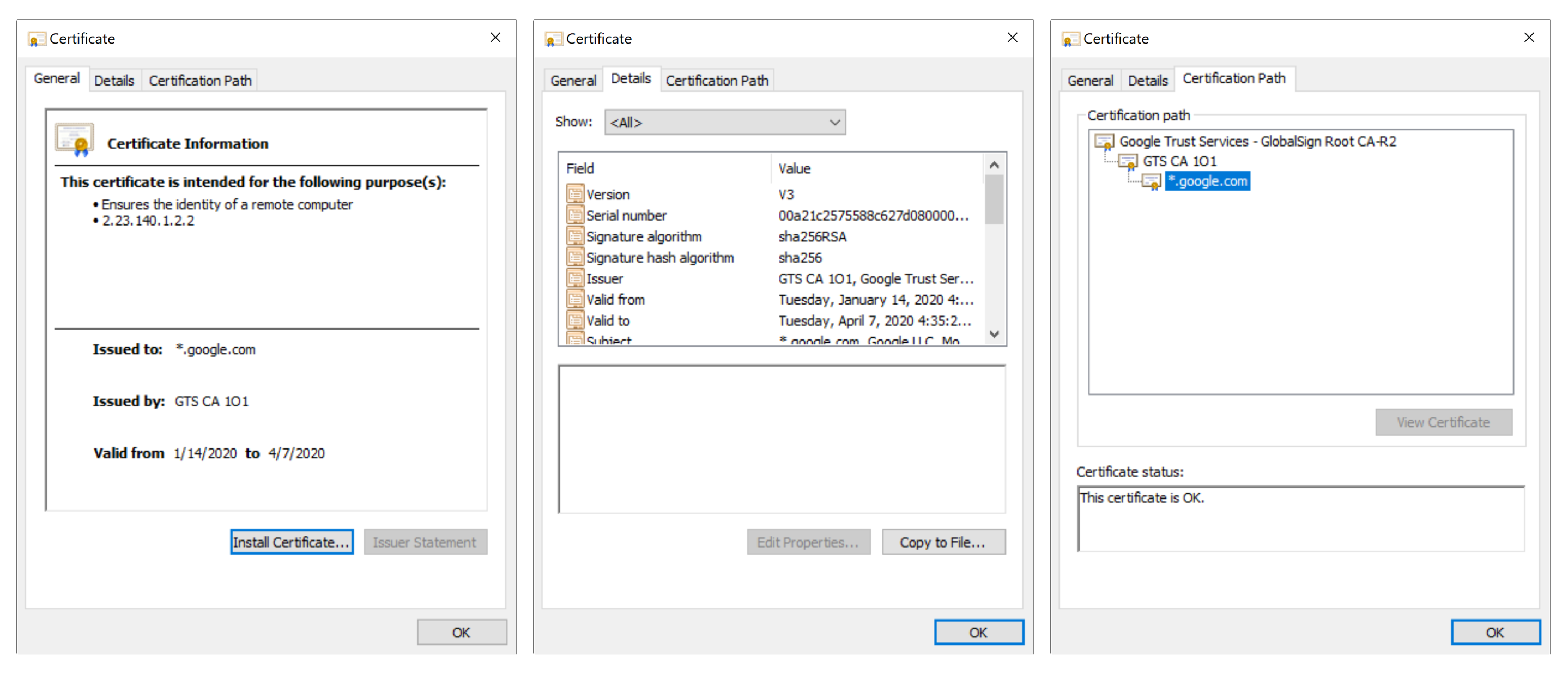
ตัวอย่าง X.509 Certificate ของ Google
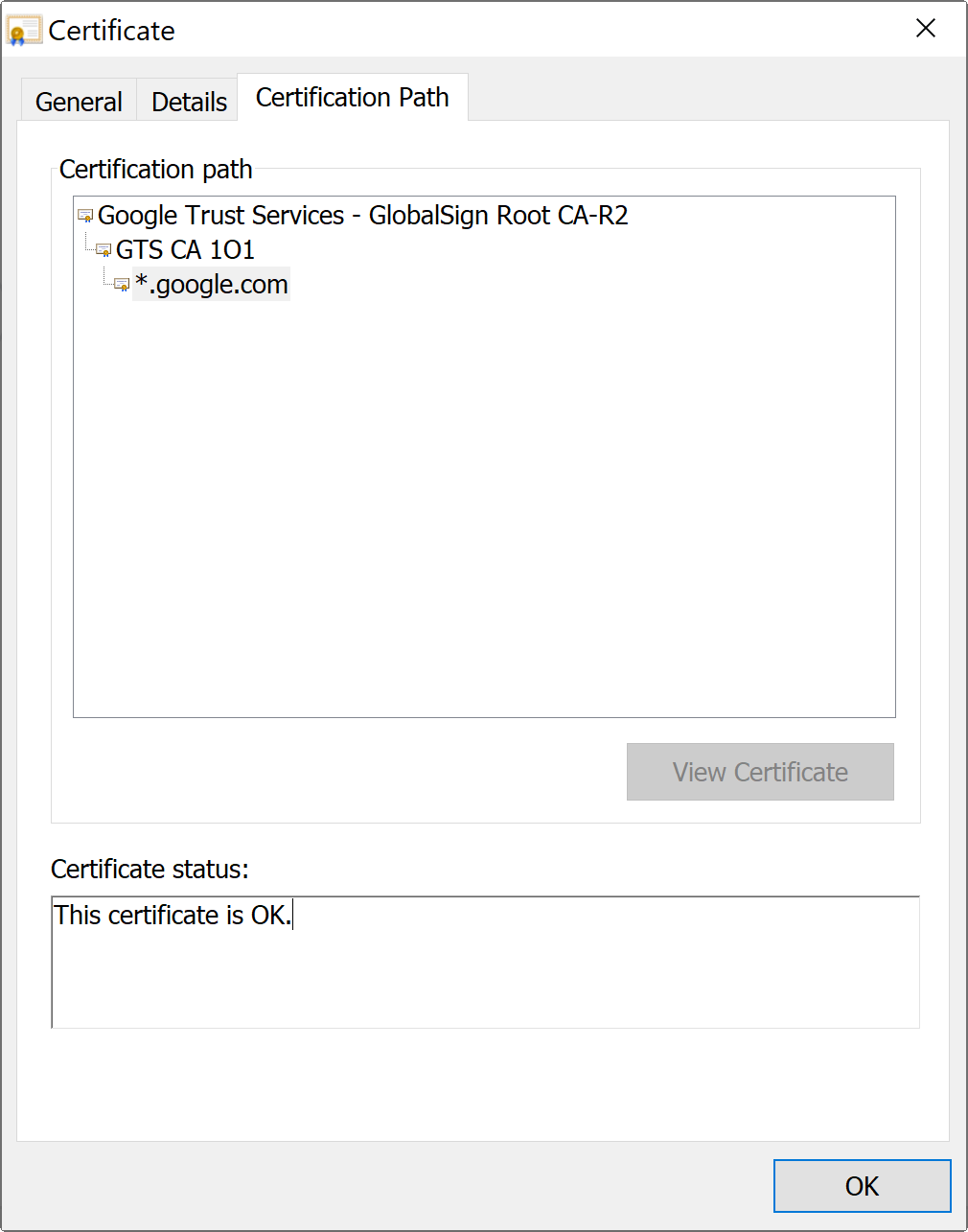
เราจะเห็นว่า X.509 Certificate ของ Google (*.google.com) ถูกรับรองโดย CA ชื่อ GTS CA 1O1 และ CA GTS CA 1O1 ก็ถูกรับรองอีกทีโดย CA ที่ชื่อว่า Google Trust Services - GlobalSign Root CA-R2
ถ้า X.509 Certificate ของ CA ที่ลงลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอลให้เรา ได้รับการรับรองที่ถูกต้อง หรือ Trust
X.509 Certificate ที่เราถืออยู่ ก็จะ Trust ตามไปด้วย
แต่ถ้า X.509 Certificate ของ CA ที่ลงลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอลให้เรา ยังไม่ Trust ก็จะทำการเช็ค X.509 Certificate ของ CA ที่อยู่เหนือขึ้นไป จนกว่าจะถึง X.509 Certificate ของ CA ชั้นบนสุด หรือ Root CA
ถ้า X.509 Certificate ของ Root CA Trust แล้ว X.509 Certificate ชั้นด้านล่าง ก็จะ Trust ตามไปด้วย
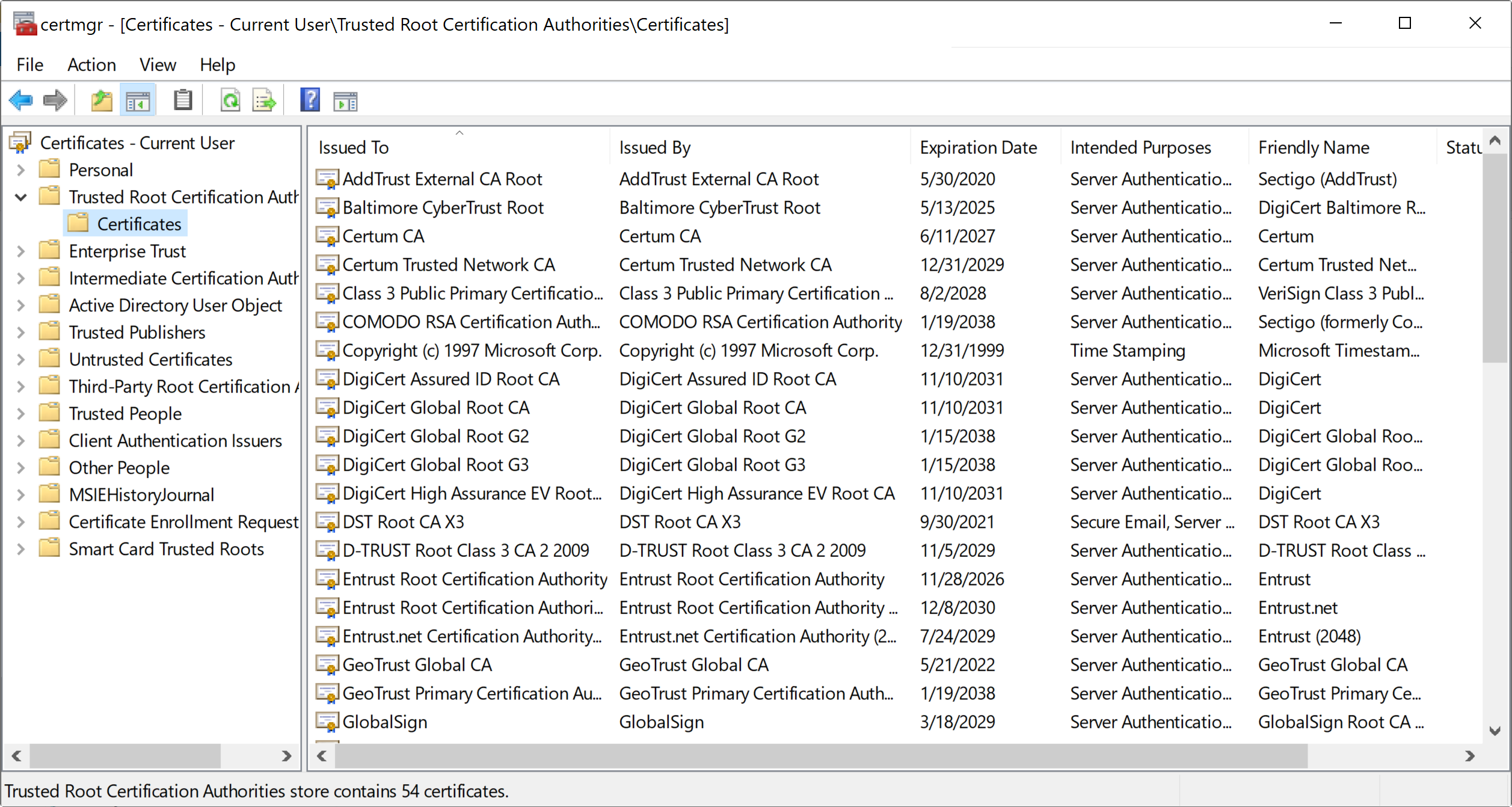
ในอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ต่าง ๆ หรือเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์ที่เราใช้งานอยู่ มักจะมี X.509 Certificate ของ Root CA ต่าง ๆ Install อยู่
ถ้าผู้ออก Certificate ให้เรา (Issuer) ได้รับการรับรองจาก Root CA นี้ X.509 Certificate ของเราก็จะได้รับความน่าเชื่อถือตามไปด้วย
mmc ที่ Windows Taskbar จากนั้นเลือกเมนู File > Add or Remove Snap-ins > Certificates > Add > My user account > Finish > OKทุกคนน่าจะคุ้นเคยกับ https ซึ่งเป็น Protocol ที่ใช้ในการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลสำหรับ Website ซึ่งมีความปลอดภัยกว่าการใช้ http ธรรมดา ๆ
X.509 Certificate คือ Certificate ที่ใช้สำหรับการทำ https
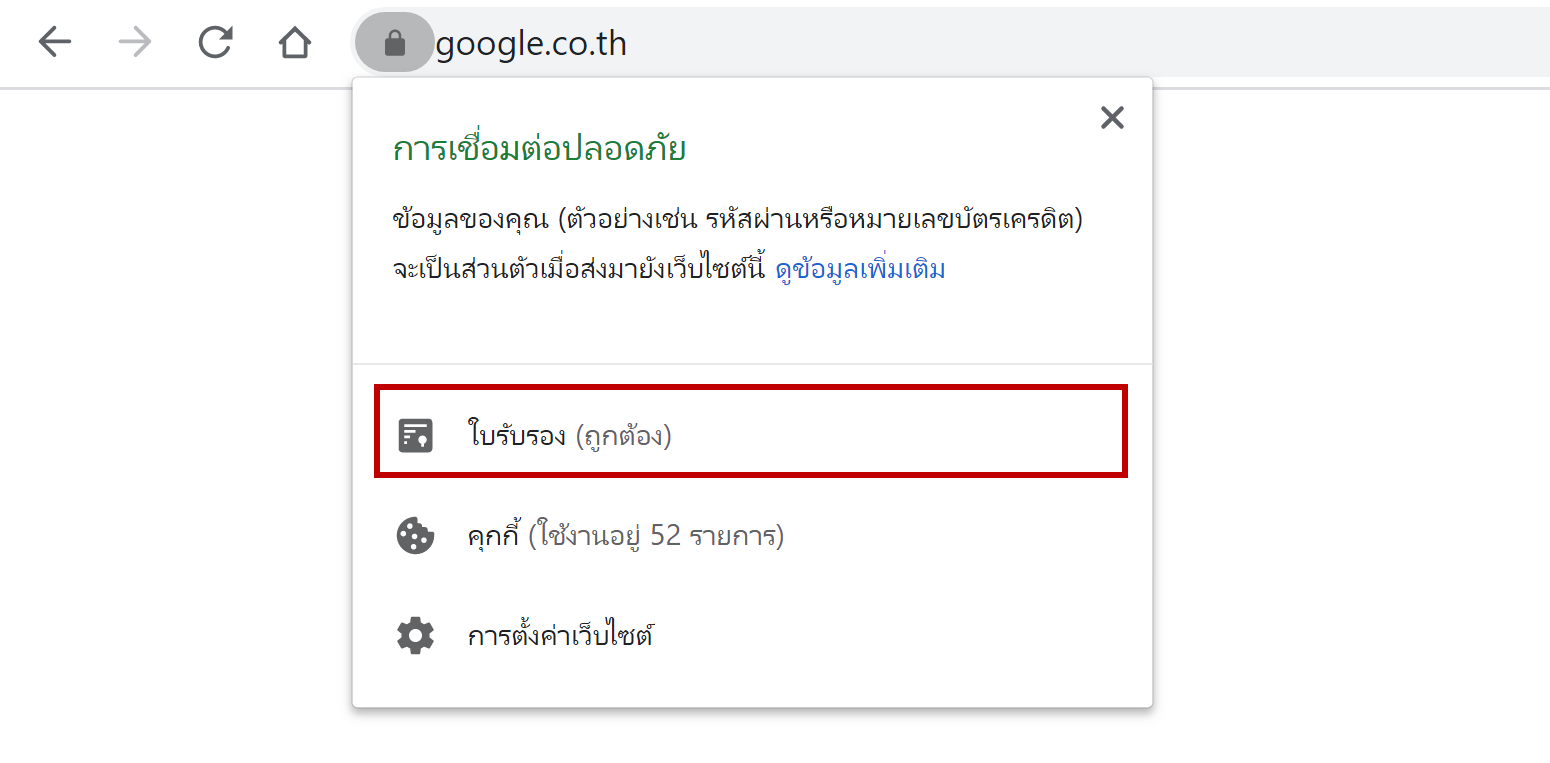
ใช้สำหรับ รับรองความถูกต้องของ Server ปลายทาง ที่ Browser หรือ Application ต้องการที่จะแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลด้วย ว่ามีความถูกต้อง เชื่อถือได้
บางครั้งเราจะเรียก Certificate ที่ใช้งานในลักษณะนี้ว่า SSL Certificate
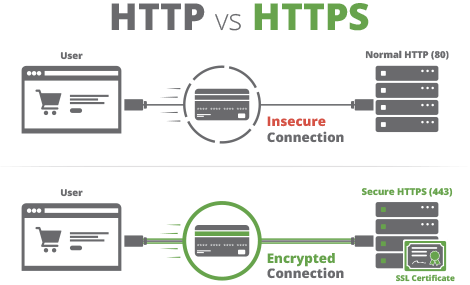
สามารถอ่านบทความเกี่ยวกับ https ได้จาก
นอกจากจะใช้ทำ https แล้ว เรายังสามารถนำ X.509 Certificate ไปใช้ทำอย่างอื่นได้อีก เช่น
ตัวอย่างการใช้ X.509 Certificate ในการทำลายเซ็นต์ดิจิตอลบน pdf เพื่อรับรองข้อมูลผู้ลงลายเซ็นต์ (Sign) ใน pdf ฉบับนี้
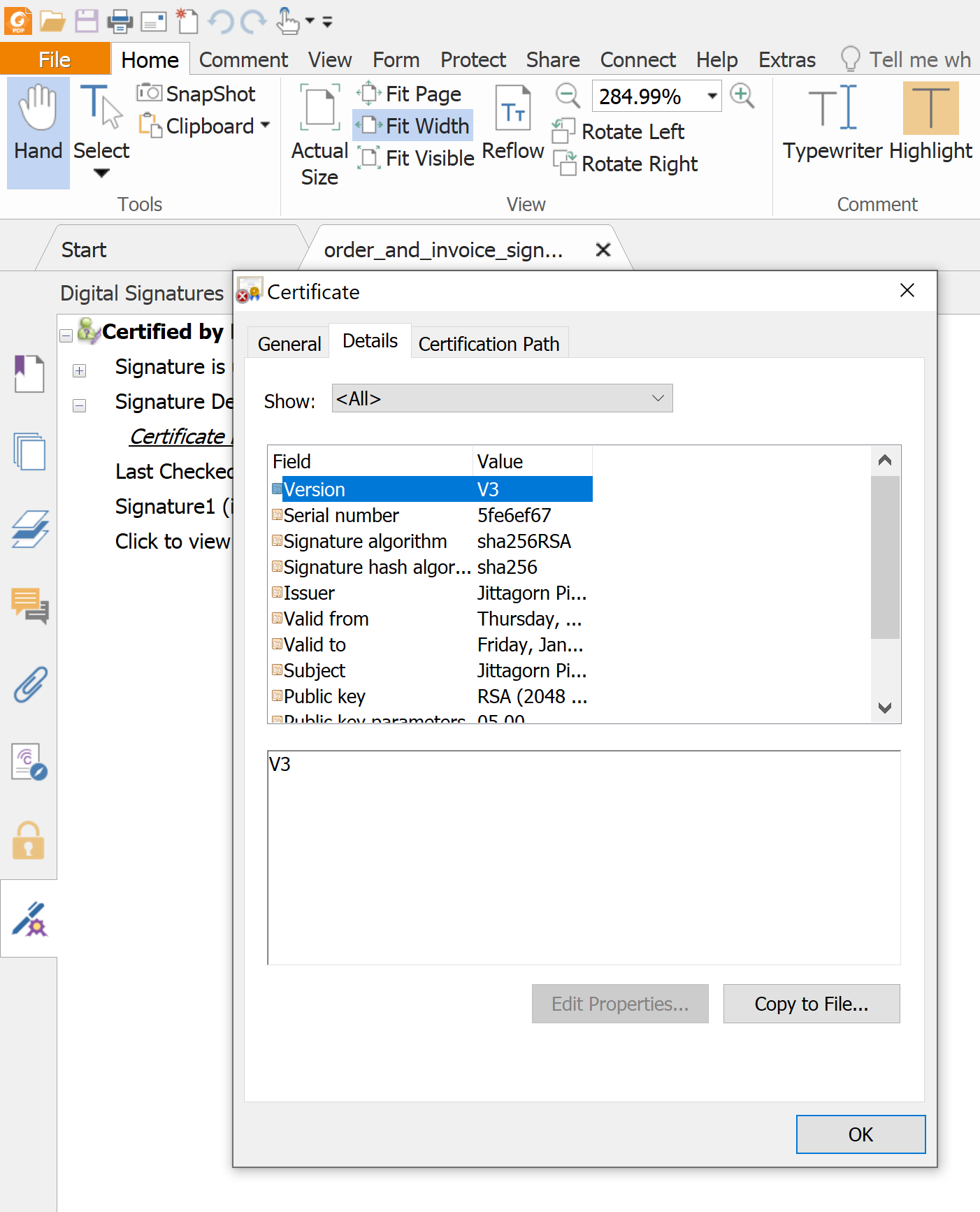
X.509 Certificate ถูกออกโดยหน่วยงานที่เรียกว่า CA (Certification Authority) หรือ เรียกเป็นภาษาไทยว่า ผู้ให้บริการออกใบรับรองอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ เป็นหน่วยงานที่ได้รับการรับรอง และมีความน่าชื่อถือ ทำหน้าที่เกี่ยวกับเรื่อง Digital Certificate โดยเฉพาะ ทั้ง
ซึ่งเราสามารถที่จะไปขอ X.509 Certificate จาก CA ต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่ได้
นอกจากการไปขอ X.509 Certificate จาก CA แล้ว เราสามารถที่จะสร้าง X.509 Certificate ขึ้นมาใช้งานเองได้ โดยการใช้เครื่องมือต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่ช่วย Gen ขึ้นมา เช่น OpenSSL หรือ Java Keytool เป็นต้น
เราเรียก Certificate ที่ Gen ขึ้นมาเอง และรับรองเองแบบนี้ว่า Self-Signed Certificate
สามารถเรียนรู้การใช้ Java Keytool ในการ Gen X.509 Certificate ได้จากบทความนี้
การใช้งาน Self-Signed Certificate มีเรื่องที่ต้องทำความเข้าใจ คือ เมื่อเรานำ Self-Signed Certificate ไปใช้งานกับธุรกรรมต่าง ๆ บนอินเตอร์เน็ต Certificate ที่เรา Gen ขึ้นมาเองนั้น จะไม่ได้รับความน่าเชื่อถือ เหมือนกับการไปขอจาก CA ดังรูป
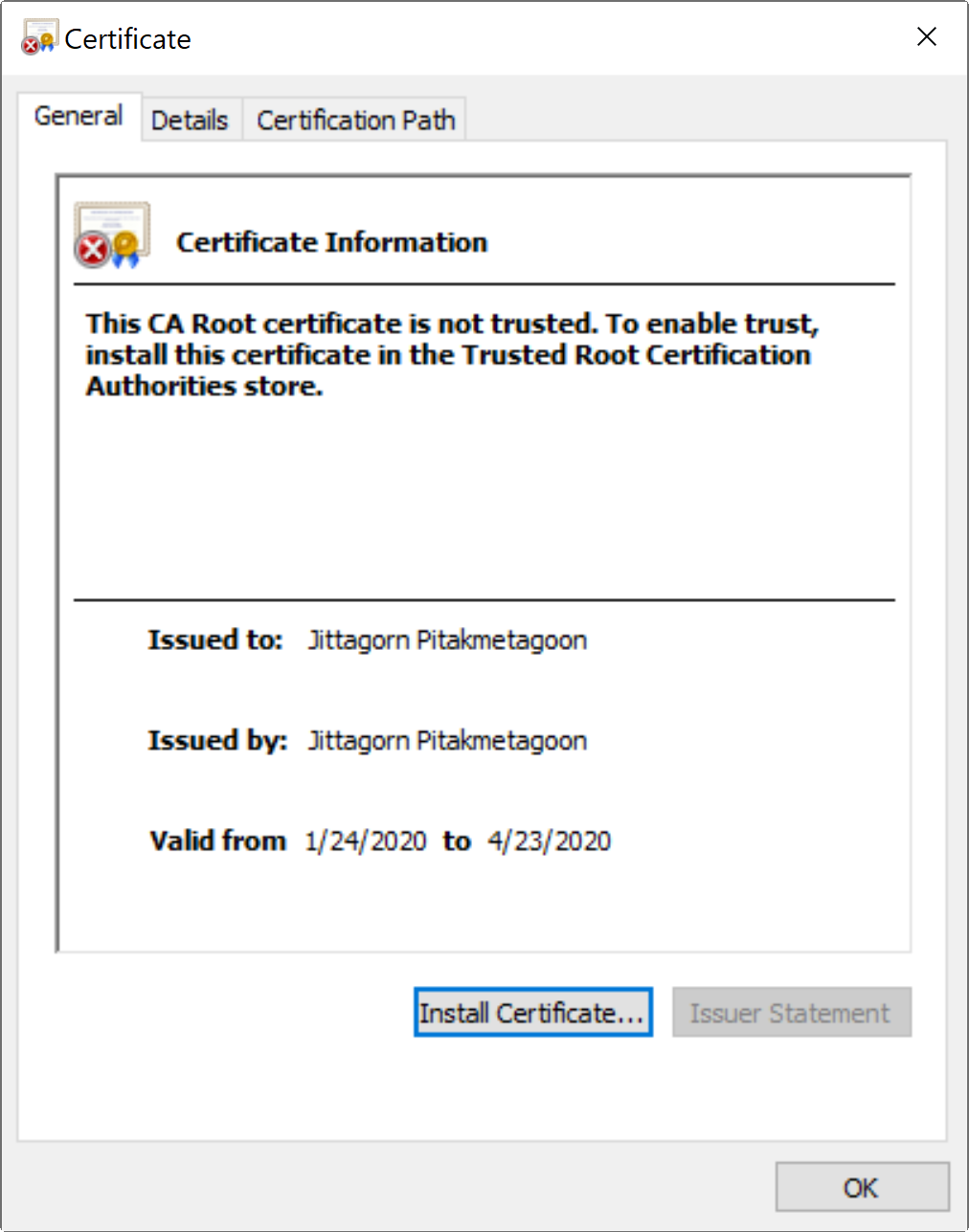
มีข้อความแจ้งเตือนว่า
This CA Root certificate not trusted. To enable trust, install this certificate in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.
สมมติ ว่าเรานำ Self-Signed Certificate ไปใช้งานกับ Web Server
Browser จะมีการแจ้งเตือนว่า การเชื่อมต่ออาจไม่ปลอดภัย ดังรูป
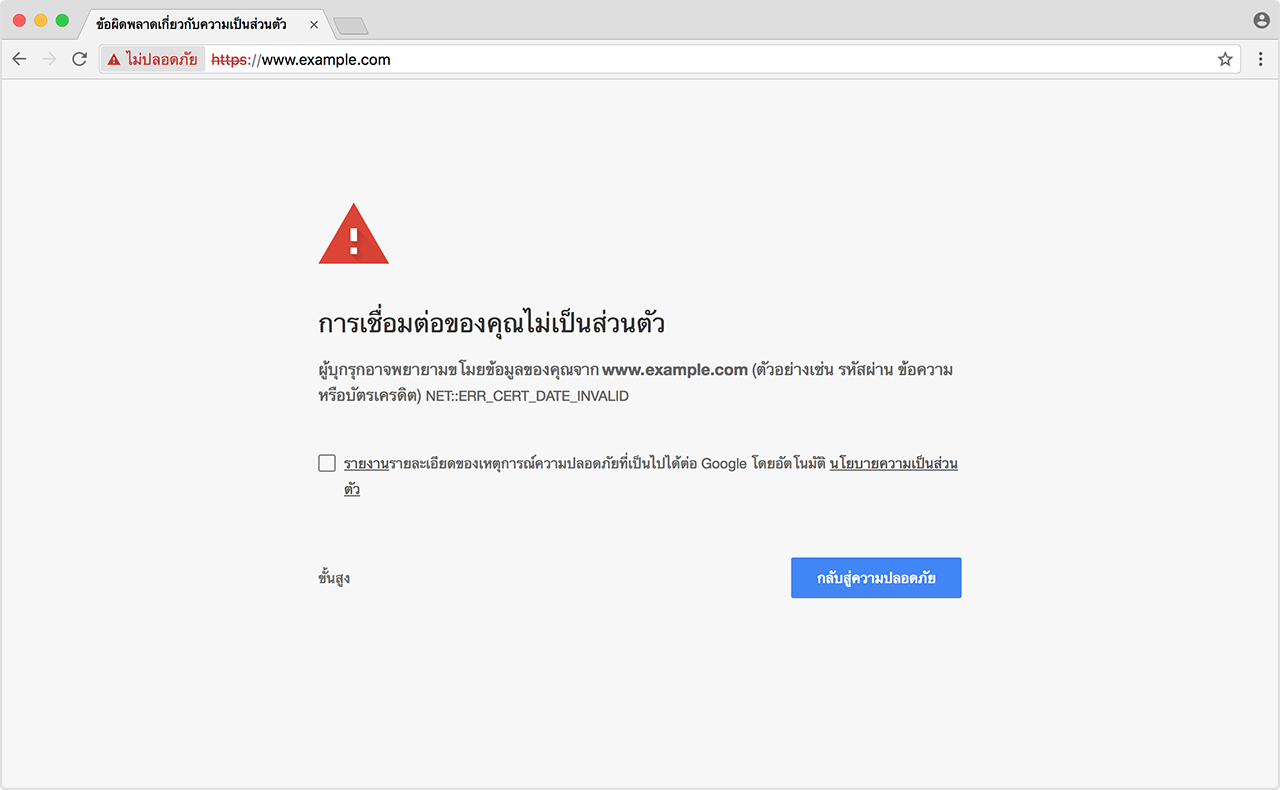
เราต้องยอมรับ/ไว้วางใจ (Trust) Certificate นั้นด้วยตัวเอง
ประกอบไปด้วย
ประกอบไปด้วย
ตอนที่เราทำการ Gen Certificate หรือ Gen Certificate Signing Request (CSR) เพื่อเอาไปขอ Certificate จาก CA ต่อ มันจะให้เรากรอกข้อมูลพวกนี้เพื่อเอาไปแปะบน Certificate
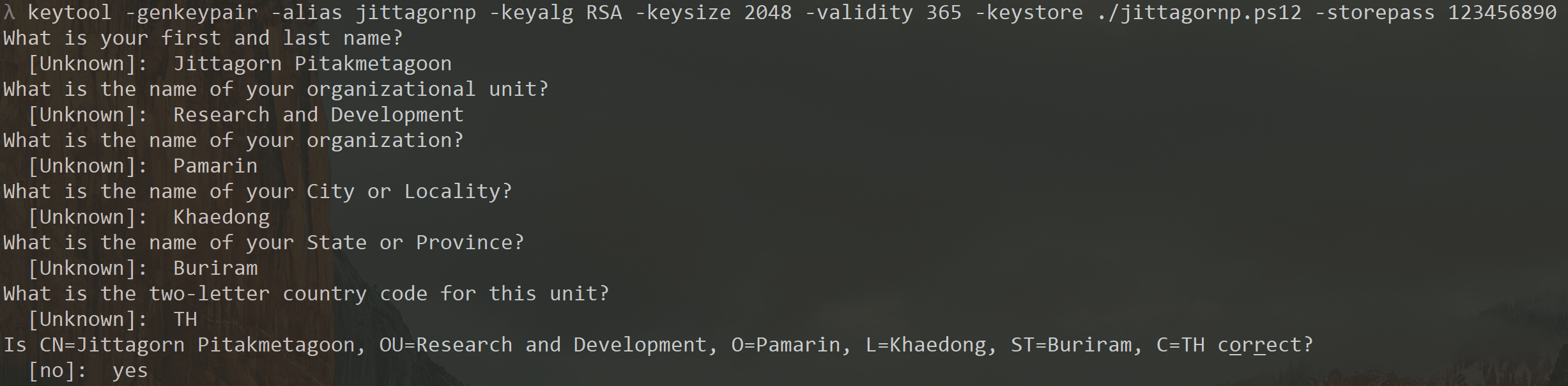
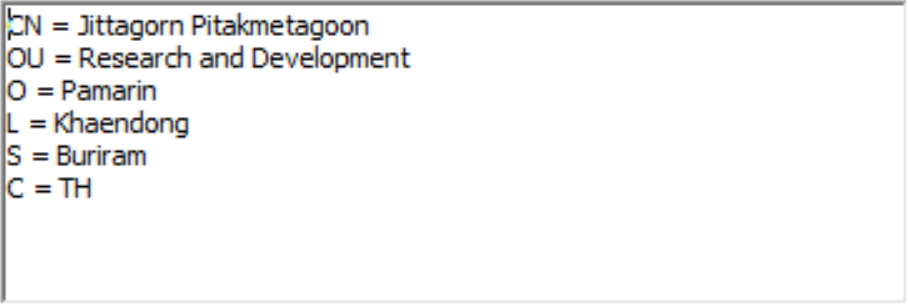
ตัวอย่างข้อมูล DN


X.509 Certificate สามารถจัดเก็บไว้ได้หลายวิธี เช่น
.pem (Privacy-enhanced Electronic Mail).der (Distinguished Encoding Rules).cer (Canonical Encoding Rules) หรือ.crtตัวอย่างไฟล์ .cer ของ X.509 Certificate
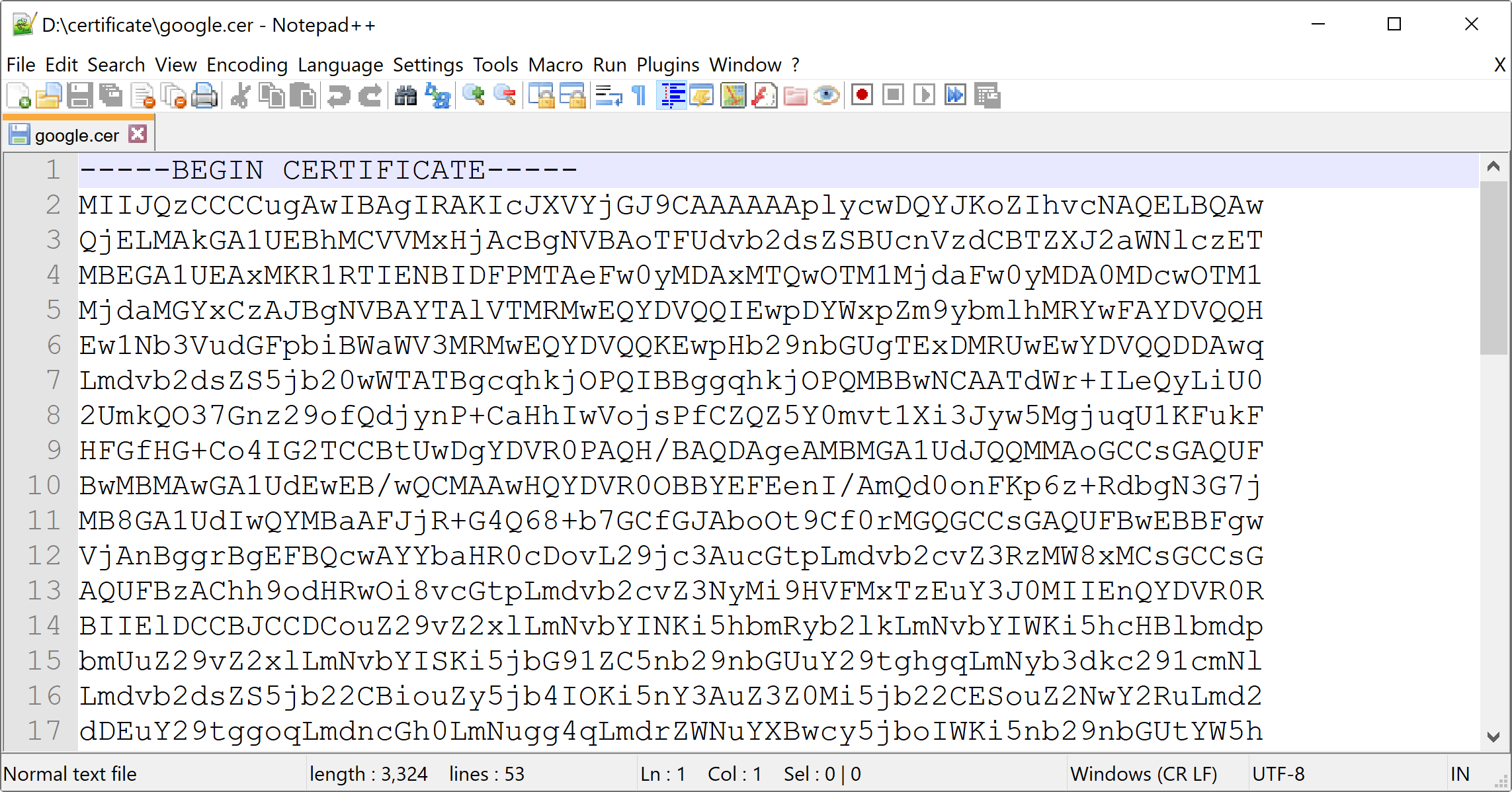
ถ้าเราลองเอาไฟล์ .cer มาเปิดดู จะพบว่าข้างในเป็น Base64 ที่เก็บข้อมูล Certificate ไว้ดังนี้
รูปแบบ Content File จะเป็น
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIJQzCCCCugAwIBAgIRAKIcJXVYjGJ9CAAAAAAplycwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAw
QjELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxHjAcBgNVBAoTFUdvb2dsZSBUcnVzdCBTZXJ2aWNlczET
....
...
MVu83sJV3ww6XiSs4LL/31e+jKZ78Cc=
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
ถ้าเราลองเอา Base64 นี้ไป Decode ดู จะได้ค่าเป็นข้อมูล Certificate ประมาณนี้

สามารถกดดู และ Download Certificate ได้จาก Address Bar ของ Browser ตรงรูปกุญแจ
/*
* Copyright 2020-Current jittagornp.me
*/
package me.jittagornp.learning.java.certificate;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.security.auth.x500.X500Principal;
/**
* @author jittagornp
*/
public class X509CertificateLearning {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CertificateException, IOException {
try ( InputStream certificateInputStream = X509CertificateLearning.class.getResourceAsStream("/google.cer")) {
final CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
final X509Certificate certificate = (X509Certificate) certificateFactory.generateCertificate(certificateInputStream);
//basic info
final String type = certificate.getType();
final int version = certificate.getVersion();
final BigInteger serialNumber = certificate.getSerialNumber();
final Date notBefore = certificate.getNotBefore();
final Date notAfter = certificate.getNotAfter();
final byte[] encoded = certificate.getEncoded();
final byte[] tbsCertificate = certificate.getTBSCertificate();
//public key
final PublicKey publicKey = certificate.getPublicKey();
final String publicKeyAlgorithm = publicKey.getAlgorithm();
final String publicKeyFormat = publicKey.getFormat();
final byte[] publicKeyEncoded = publicKey.getEncoded();
//signature
final String sigAlgName = certificate.getSigAlgName();
final String sigAlgOID = certificate.getSigAlgOID();
final byte[] sigAlgParams = certificate.getSigAlgParams();
final byte[] signature = certificate.getSignature();
//issuer
final Principal issuerDN = certificate.getIssuerDN();
final boolean[] issuerUniqueID = certificate.getIssuerUniqueID();
final X500Principal issuerX500Principal = certificate.getIssuerX500Principal();
final byte[] issuerX500PrincipalEncoded = issuerX500Principal.getEncoded();
final Collection<List<?>> issuerAlternativeNames = certificate.getIssuerAlternativeNames();
//subject
final Principal subjectDN = certificate.getSubjectDN();
final boolean[] subjectUniqueID = certificate.getSubjectUniqueID();
final X500Principal subjectX500Principal = certificate.getSubjectX500Principal();
final Collection<List<?>> subjectAlternativeNames = certificate.getSubjectAlternativeNames();
//key usage
final boolean[] keyUsage = certificate.getKeyUsage();
final List<String> extendedKeyUsage = certificate.getExtendedKeyUsage();
//others
final int basicConstraints = certificate.getBasicConstraints();
final Set<String> criticalExtensionOIDs = certificate.getCriticalExtensionOIDs();
final Set<String> nonCriticalExtensionOIDs = certificate.getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs();
System.out.println("Basic");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("String type => " + type);
System.out.println("int version => " + version);
System.out.println("BigInteger serialNumber => " + serialNumber);
System.out.println("Date notBefore => " + notBefore);
System.out.println("Date notAfter => " + notAfter);
System.out.println("byte[] encoded length => " + encoded.length);
System.out.println("byte[] tbsCertificate length => " + tbsCertificate.length);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Public Key");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("String publicKey.algorithm => " + publicKeyAlgorithm);
System.out.println("String publicKey.format => " + publicKeyFormat);
System.out.println("byte[] publicKey.encoded length => " + publicKeyEncoded.length);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Signature");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("String sigAlgName => " + sigAlgName);
System.out.println("String sigAlgOID => " + sigAlgOID);
System.out.println("byte[] sigAlgParams => " + sigAlgParams);
System.out.println("byte[] signature length => " + signature.length);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Issuer");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Principal issuerDN => " + issuerDN);
System.out.println("boolean[] issuerUniqueID => " + issuerUniqueID);
System.out.println("X500Principal issuerX500Principal => " + issuerX500Principal);
System.out.println("byte[] issuerX500Principal.encoded length => " + issuerX500PrincipalEncoded.length);
System.out.println("Collection<List<?>> issuerAlternativeNames => " + issuerAlternativeNames);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Subject");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Principal subjectDN => " + subjectDN);
System.out.println("boolean[] subjectUniqueID => " + subjectUniqueID);
System.out.println("X500Principal subjectX500Principal => " + subjectX500Principal);
System.out.println("Collection<List<?>> subjectAlternativeNames => " + subjectAlternativeNames);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Key Usage");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("boolean[] keyUsage length => " + keyUsage.length);
System.out.println("List<String> extendedKeyUsage => " + extendedKeyUsage);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Others");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("int basicConstraints => " + basicConstraints);
System.out.println("Set<String> criticalExtensionOIDs => " + criticalExtensionOIDs);
System.out.println("Set<String> nonCriticalExtensionOIDs => " + nonCriticalExtensionOIDs);
}
}
}
output
Basic
----------------------------------------------------
String type => X.509
int version => 3
BigInteger serialNumber => 215481079375450091442107987479044396839
Date notBefore => Tue Jan 14 16:35:27 ICT 2020
Date notAfter => Tue Apr 07 16:35:27 ICT 2020
byte[] encoded length => 2375
byte[] tbsCertificate length => 2095
Public Key
----------------------------------------------------
String publicKey.algorithm => EC
String publicKey.format => X.509
byte[] publicKey.encoded length => 91
Signature
----------------------------------------------------
String sigAlgName => SHA256withRSA
String sigAlgOID => 1.2.840.113549.1.1.11
byte[] sigAlgParams => null
byte[] signature length => 256
Issuer
----------------------------------------------------
Principal issuerDN => CN=GTS CA 1O1, O=Google Trust Services, C=US
boolean[] issuerUniqueID => null
X500Principal issuerX500Principal => CN=GTS CA 1O1, O=Google Trust Services, C=US
byte[] issuerX500Principal.encoded length => 68
Collection<List<?>> issuerAlternativeNames => null
Subject
----------------------------------------------------
Principal subjectDN => CN=*.google.com, O=Google LLC, L=Mountain View, ST=California, C=US
boolean[] subjectUniqueID => null
X500Principal subjectX500Principal => CN=*.google.com, O=Google LLC, L=Mountain View, ST=California, C=US
Collection<List<?>> subjectAlternativeNames => [[2, *.google.com], [2, *.android.com], [2, *.appengine.google.com], [2, *.cloud.google.com], [2, *.crowdsource.google.com], [2, *.g.co], [2, *.gcp.gvt2.com], [2, *.gcpcdn.gvt1.com], [2, *.ggpht.cn], [2, *.gkecnapps.cn], [2, *.google-analytics.com], [2, *.google.ca], [2, *.google.cl], [2, *.google.co.in], [2, *.google.co.jp], [2, *.google.co.uk], [2, *.google.com.ar], [2, *.google.com.au], [2, *.google.com.br], [2, *.google.com.co], [2, *.google.com.mx], [2, *.google.com.tr], [2, *.google.com.vn], [2, *.google.de], [2, *.google.es], [2, *.google.fr], [2, *.google.hu], [2, *.google.it], [2, *.google.nl], [2, *.google.pl], [2, *.google.pt], [2, *.googleadapis.com], [2, *.googleapis.cn], [2, *.googlecnapps.cn], [2, *.googlecommerce.com], [2, *.googlevideo.com], [2, *.gstatic.cn], [2, *.gstatic.com], [2, *.gstaticcnapps.cn], [2, *.gvt1.com], [2, *.gvt2.com], [2, *.metric.gstatic.com], [2, *.urchin.com], [2, *.url.google.com], [2, *.wear.gkecnapps.cn], [2, *.youtube-nocookie.com], [2, *.youtube.com], [2, *.youtubeeducation.com], [2, *.youtubekids.com], [2, *.yt.be], [2, *.ytimg.com], [2, android.clients.google.com], [2, android.com], [2, developer.android.google.cn], [2, developers.android.google.cn], [2, g.co], [2, ggpht.cn], [2, gkecnapps.cn], [2, goo.gl], [2, google-analytics.com], [2, google.com], [2, googlecnapps.cn], [2, googlecommerce.com], [2, source.android.google.cn], [2, urchin.com], [2, www.goo.gl], [2, youtu.be], [2, youtube.com], [2, youtubeeducation.com], [2, youtubekids.com], [2, yt.be]]
Key Usage
----------------------------------------------------
boolean[] keyUsage length => 9
List<String> extendedKeyUsage => [1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1]
Others
----------------------------------------------------
int basicConstraints => -1
Set<String> criticalExtensionOIDs => [2.5.29.15, 2.5.29.19]
Set<String> nonCriticalExtensionOIDs => [1.3.6.1.4.1.11129.2.4.2, 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.1.1, 2.5.29.14, 2.5.29.17, 2.5.29.31, 2.5.29.32, 2.5.29.35, 2.5.29.37]
อันนี้เป็นบทความที่อธิบาย X.509 Certificate Chain ได้ดีมากครับ